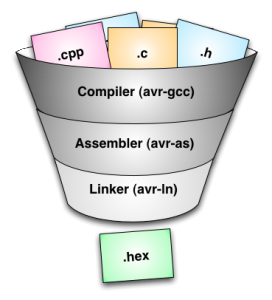
A Toolchain is the set of Programming Tools that are used to create software. The Tools are used in a chain , so that the output of each tool becomes the input for the next tool.
Editor:
Editor is program in which we can write our code and edit that code. Gedit , kwrite are the examples of editors.
File name : Demo.c
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAX 10
int Add(int No1, int No2)
{
Int Ans; //Local Variable
Ans = No1 + No2 + MAX ;
printf(“Addition of Two Numbers is %d”,Ans);
return Ans;
}
Pre-processor:
The Pre-processors provide the ability for the inclusion of header files, macro expantion, conditional compilation,and line control.
Pre-processor takes lines beginning with ‘#’ as a directives. Because it does not know about the underlying language.
After Preprocessing it will give the expanded code as a output having extension .i.
File name : Demo.i
int printf( const char * format, …);
int scanf( const char * format, …);
int Add(int No1, int No2)
{
int Ans;
Ans = No1 + No2 + 10 ;
printf(“Addition of Two Numbers is %d”,Ans);
return Ans;
}
Compiler :
Compiler is the program which is used for translating source code from a high level programming language (like c,c++) to lower level programming language (like machine language).So, in this case we consider that output is in assembly language having extention .asm or .s.File name : Demo.asmAdd: PUSH ECX PUSH EDX ADD ECX,EDX ADD ECX,10 MOV EAX,ECXRETN
Assembler :
Assembler is a program which translates assembly language program to an object file , which
contains the code in machine language. Object file does contain the machine code but still it is non-executable.
Extention of object file is .obj.
File name : Demo.obj
10110110111000101001010
10101110100010100101010
10111011101110101110110
00101110111011101110101
00100010000100001001010
10111011101110110111101
01000100001111101110101
Linker :
A Linker is a program which takes one or more object files and combines them into a single
executable program having extension .exe.
File name : Demo.exe
Demo.obj Other.obj
10110110111000101001110 10100110111000101001010
10101110100010100001010 10110111111000101001010
10111011101110101010110 10110110111000101001011
10101110111011101110101 + 00100010000100001001110
10100010000100001001010 00100010000100001001011
00111011101110110111101 00100010000100001001011
11000100001111101110101 10111011101110101110111
Demo.exe
10101110100010100101010
10111011101110101110110
00101110111011101110101
00100010000100001001010
10111011101110110111101
01000100001111101110101
10101110100010100101010
10111011101110101110110
00101110111011101110101
00100010000100001001010
10111011101110110111101
01000100001111101110101
Loader :
A Loader is a program which is the part of OS i.e. operating system that is responsible for loading programs.
It places program in memory (RAM) and prepares them for the execution and loading a program
involves reading a contents of an executable file like text , data into the memory.
Demo.exe running in RAM
10101110100010100101010
10111011101110101110110
00101110111011101110101
00100010000100001001010
10111011101110110111101
01000100001111101110101
10101110100010100101010
10111011101110101110110
00101110111011101110101
00100010000100001001010
10111011101110110111101
01000100001111101110101
Set of the Commands which will elaborate the Toolchain components :-
Step 1. Create a file name as Demo.c which contains simple C program.
Step 2. Compile that file using command
# gcc -S -o Demo.S Demo.c
This command gives output file in assembly language named as Demo.S
Step 3. Pass that Assembly file to assembler which gives output as a object file named as
Demo.o
# as -o Demo.o Demo.S
Step 4. Pass that object file to Linker which gives output as a executable file.
# ld -o Demo -lc -dynamic-linker /lib/ld-linux.so.2 Demo.o -e main
Step 5. Run that executable using
# ./Demo