Wi-Fi is a Wireless technology that uses the radio frequency to transmit data through air. With the rise of Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi), technology comes the rise of the hotspot -public access Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) that allow anyone with a Wi-Fi capable notebook or PDA to connect to the Internet or a corporate intranet in airports, hotels, coffee shops, or even campgrounds and fast food restaurants.
Wi-Fi hotspots are expected to have an important role in future provisioning of “anywhere, anytime” connectivity. They are quickly being deployed at locations that tend to attract nomadic users, such as cafes, airports, hotels, and conference center. This article contributes an alternative billing architecture using virtual prepaid tokens (VPTs) and experimentally evaluates its performance.
Users buy VPTs at the point and time of access, using a third-party online payment server. Therefore, such an account is more flexible than is a conventional pay-per-use account, which can be used only to purchase access from a specific provider or set of providers. Unlike physical prepaid tokens, VPTs allow a user to order and obtain Internet access from a provider in less than 15 s, even if the user has no previous or subsequent relationship with that provider or that provider’s aggregator. Simultaneous support for captive-portal and 802.1x authentication allows hotspots to provide recent Wi-Fi security improvements to those clients whose configuration supports them, and not disrupts the legacy clients.
Wi-Fi security with 802.1 xs:
802.1X was drafted by the IEEE to provide improved access control. It was originally developed to protect switched Ethernet hub ports; however it was soon recognized that it was
Applicable to 802.11b networks as well. 802.1X is a port-based access control method that enables higher layer authentication (or ULAP – Upper Layer Authentication Protocols) to occur directly between the user and the authentication server.
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP):
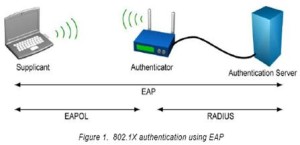
802.1X utilizes Extensible Authentication Protocol for user authentication. EAP challenge-response dialogues are sent between the client and authentication server in encapsulated EAPOL format. The access point merely relays these EAP messages between the client and an EAP-enabled authentication server (such as a RADIUS server) until an EAP success or failure message is generated, at which point it will either grant network access through the controlled port, or disconnect the user. When the authentication server has authenticated and authorized the user, dynamic session keys are assigned and forwarded to the AP. In a per-session, single sign-on, keys change often enough to prevent key cracking or passive hacking attacks.
There are a number of proprietary as well as standard EAP authentication methods that may be employed in an 802.1X architecture. For a hotspot, the most difficult part of implementing EAP is ensuring that users’ devices are equipped with any client software or certificates required for the chosen EAP method. Cisco, Microsoft, Intel, IBM and others are integrating the latest 802.1X specification into their product lines, and most users likely already have some form EAP support in their hardware.Microsoft Windows XP operating system, for example, is enabled to support PEAP.

Good…. also try to add more topics on WiFi
Thanks @3D, Stay tuned for new Techno updates…